An Easy Guide on Morphology Instruction for Language Teachers (+5 Strategies for Classroom Application)
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how some students seem to grasp word meanings effortlessly while others struggle? The secret often lies in morphology instruction, a teaching approach that breaks words into their smallest meaningful parts. While some may not be familiar with this method, it has been proven helpful for building vocabulary, improving reading comprehension, and enhancing writing skills.
By teaching students to understand how words are constructed, morphology instruction equips them with the tools to decode language and approach unfamiliar words with confidence.
Before we dive deeper into what makes this method so effective, here are a few key points to help you understand morphology instruction at a glance:
- Morphology focuses on word parts. It teaches students to identify roots, prefixes, and suffixes and how they combine to form words.
- Roots are the base of meaning. These are the core parts of words that carry the main idea or definition.
- Prefixes and suffixes modify words. Prefixes are added to the beginning, and suffixes are added to the end of roots to adjust their meaning or function.
- It’s about patterns in language. Morphology helps students recognize common word structures, making it easier to decode unfamiliar vocabulary.
What is Morphology? (Let’s Keep it Simple!)
Morphology is the study of the smallest meaningful units of language, called morphemes. These include roots, prefixes, and suffixes which are technically pieces that come together to form words. Understanding morphology means breaking down words into these parts to uncover their meaning and how they function in sentences.
For example, in the word “unhappiness”:
- Un- is a prefix meaning “not”
- Happy is the root word
- ness is a suffix that turns the adjective into a noun
Together, these morphemes create the full meaning: “the state of not being happy.”
Morphology instruction teaches students to analyze words in this way. By understanding how morphemes work, they can approach unfamiliar words with confidence.
Here are more examples:
- Rebuild
- Re- (prefix) means “again”
- Build (root) is the base word
- Full meaning: “to build again.”
- Comfortable
- Comfort (root) means “ease”
- able (suffix) means “capable of”
- Full meaning: “capable of providing ease.”
- Disorganized
- Dis- (prefix) means “not”
- Organize (root) means “to arrange”
- ed (suffix) indicates past tense
- Full meaning: “not arranged or put in order.”
Key Components of Morphology Instruction
Morphology instruction is built on a few essential components that help students understand and apply the structure of words. These elements work together to create a comprehensive approach to decoding language:
- Morphemes Morphemes are the building blocks of words. They include:
- Roots: The core meaning of a word (e.g., “bio” in “biology” means “life”).
- Prefixes: Added to the beginning of a root to change its meaning (e.g., “un-” in “unhappy” means “not”).
- Suffixes: Added to the end of a root to modify its function (e.g., “-ly” in “happily” makes the word an adverb).
- Word Analysis Students learn to break words into their morphemes to determine their meaning. For example:
- “Misunderstanding” = Mis- (wrong) + understand (root) + ing (action).
- Pattern Recognition Morphology instruction teaches students to identify patterns in words, making it easier to decode unfamiliar terms. For instance:
- Words with the prefix “trans-” (across) often relate to movement or change, like “transport” or “transform.”
- Morphological Families Students are introduced to groups of words that share the same root to expand their vocabulary. For example:
- From the root “dict” (to say): predict, dictate, dictionary, contradict.
Why Did Morphology Become a Teaching Method?
Morphology didn’t just emerge as an instructional strategy by chance. It became essential because of its direct impact on literacy development. Educators realized that many students struggle with vocabulary and comprehension, not because they lack intelligence, but because they lack the tools to decode complex words.
Traditional methods of teaching vocabulary often relied on memorization, which only works for a limited number of words. Morphology instruction offers a deeper, more systematic approach.
| Traditional Vocabulary Teaching | Morphology Instruction |
|---|---|
| Focus: Teaches a fixed list of vocabulary words for students to memorize. | Focus: Breaks down words into roots, prefixes, and suffixes, teaching students how to build and decode meaning. |
| Scope: Limited to the words explicitly taught in class. | Scope: Equips students to understand thousands of unfamiliar words using structural analysis. |
| Method: Relies on repetition and rote memorization, often without explaining why words mean what they do. | Method: Encourages critical thinking by showing patterns and logical structures in word formation. |
| Retention: Words learned are often forgotten over time because they lack deeper understanding. | Retention: Builds long-lasting knowledge by helping students internalize patterns in language. |
| Application: Struggles to connect to real-world use beyond tests and assignments. | Application: Helps students independently decode complex texts, boosting confidence in reading and writing. |
| Example: Students memorize that “transport” means “to carry or move.” | Example: Students learn that “trans-” means “across” and “port” means “to carry,” allowing them to infer the meaning of “transport,” “portable,” and “export.” |
How Teachers Can Incorporate Morphology Instruction in Classrooms
Morphology instruction is versatile and can be seamlessly integrated into various classroom activities. By embedding these strategies into everyday lessons, teachers can help students build a strong foundation in vocabulary, reading, and comprehension. Here’s how you can start:
1. Gradually introduce morphemes.
Start by teaching common roots, prefixes, and suffixes. Introduce a manageable number of morphemes each week, focusing on their meanings and functions. This ensures students don’t feel overwhelmed while gradually building their understanding of word formation.
Example: Begin with high-frequency prefixes like “un-“ (not) and “re-“ (again), followed by roots like “struct” (build). By focusing on these basic building blocks, students gain a foundation they can build upon.
Activity: Create a “Word Tree” on the board, where you add new words each week that use the same root or prefix. For example, with “re-“, you can add:
- “revisit,”
- “rebuild,” and
- “replace.”
2. Use word-sorting activities.
Word sorts are a hands-on way for students to categorize words based on shared morphemes. By recognizing patterns in words, students strengthen their vocabulary skills and learn how to break down unfamiliar words into familiar parts.
Example: Provide students with a mix of words like “export,” “import,” “transport,” and “support,” and have them sort the words by the shared root “port.” This allows students to see how the same root can form different meanings based on the context and prefix attached.
Tip: Enhance this activity with visuals. For example, include images of ships for “transport” or “export” to help students connect the words to their meanings. Visuals make abstract concepts more tangible and memorable.
3. Incorporate morphemes in reading and writing.
Apply morphemes directly to reading and writing assignments. This gives students real-world practice and helps them see how morphemes work in authentic language use. By using morphemes in context, students can develop a deeper understanding of word meaning and structure.
Reading: Highlight morphemes in texts. For instance, when reading the word “predictable,” break it down into “pre-“ (before), “dict” (say), and “-able” (capable of). Have students identify these morphemes and discuss how they contribute to the overall meaning of the word.
Writing: Encourage students to create new words by combining morphemes. For example, “eco-“ (environment) + “friend” + “-ly” could form “ecofriendly.” This creative activity helps students understand how words evolve and the flexibility of language.
4. Create morphological word maps.
Word maps are an effective visual tool for breaking down complex words into their morphemic components. By mapping words, students can visually understand how the parts of a word contribute to its overall meaning. This also helps reinforce their understanding of morphemes and their relationships.
Example: For the word “construction,” students can break it down as:
- “Con-“ = together
- “Struct” = build
- “-ion” = action or process
This breakdown gives students a clear visual representation of how the word is formed and how its meaning is shaped by the individual morphemes.
5. Leverage technology for interactivity.
Technology offers countless opportunities to make morphology instruction more engaging and interactive. Using digital tools can turn morphology practice into an interactive experience that excites students and deepens their understanding.
Use interactive whiteboards to visually break down words during lessons, allowing students to contribute by dragging and sorting morphemes. For example, display “unsuccessful” on the board and have students break it down live into “un-“ (not), “success” (achievement), and “-ful” (full of).
You can even leverage AI. Edcafe AI, for one, has AI-powered teaching content generators that could help make morphology instruction quicker, and more interactive.
You can start with an Edcafe AI-powered quiz. In this example, I simply prompted Edcafe AI to create a quiz that would test students’ knowledge on morphology of words, structure-wise.
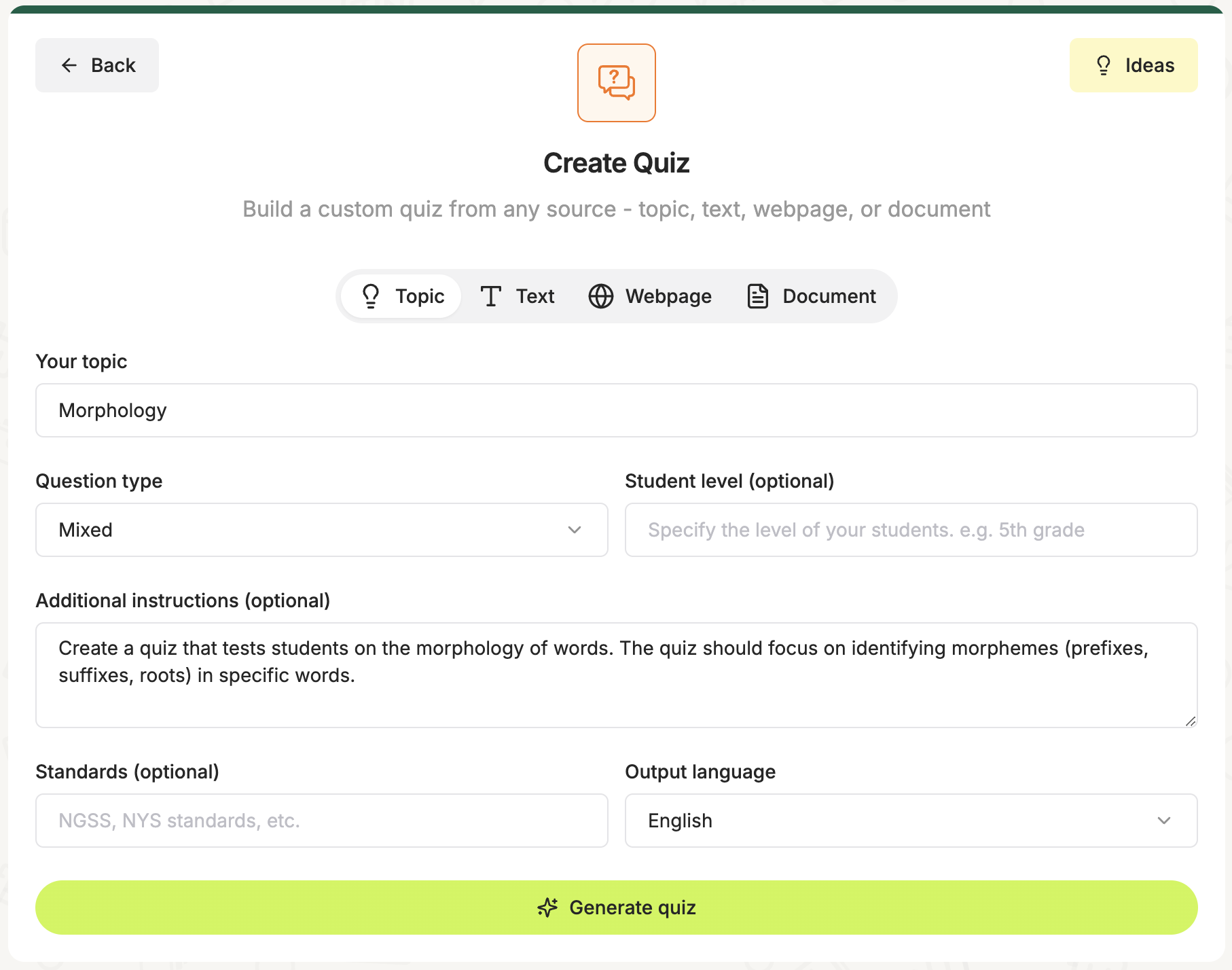
And in seconds, it was able to generate a whole quiz as it was instructed.
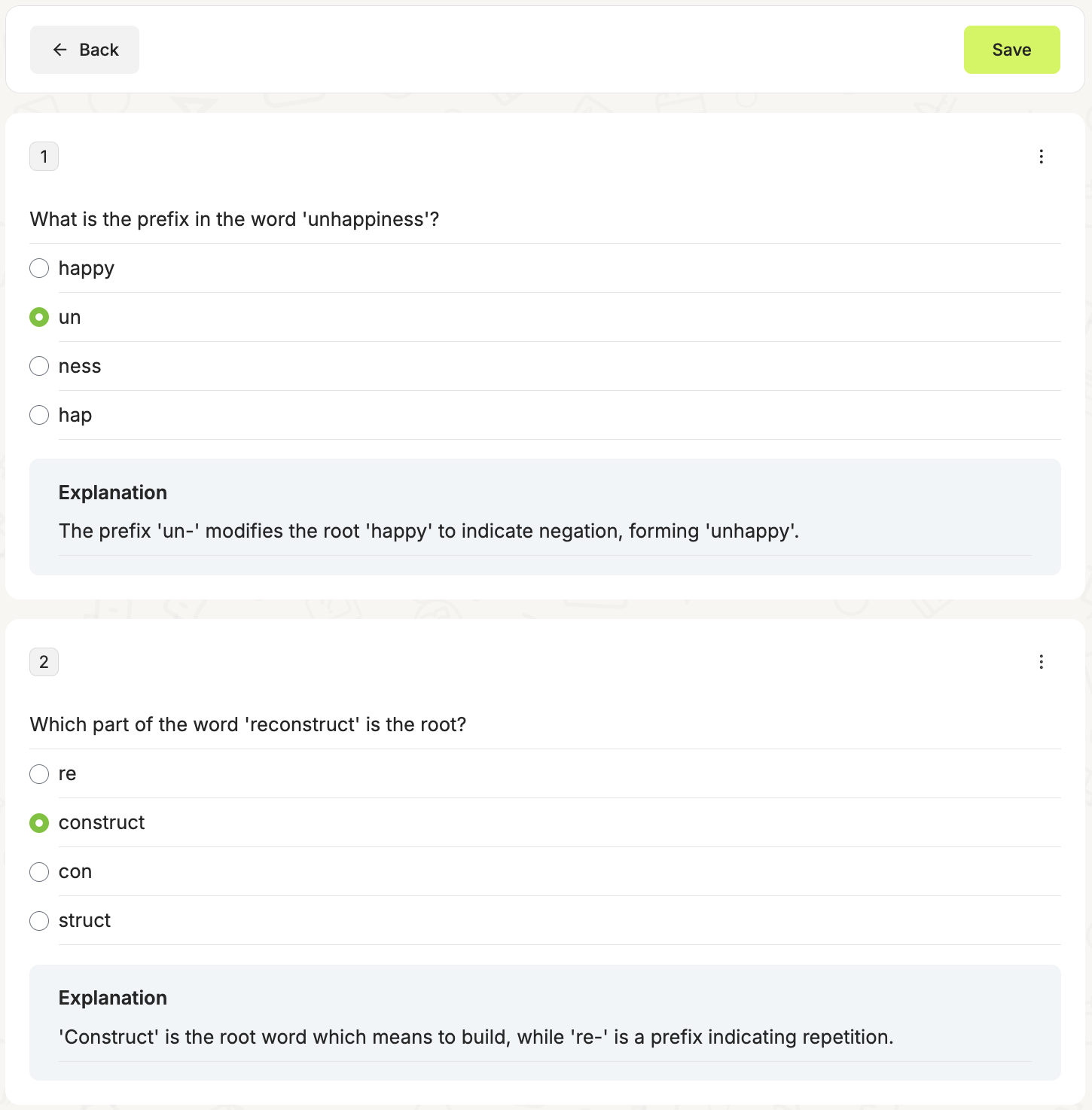
Conveniently “launch” the quiz to your students, so they can access and work on the it in a scan of a QR. This interactive feature allows them to complete the quiz right on their devices, even asynchronously.
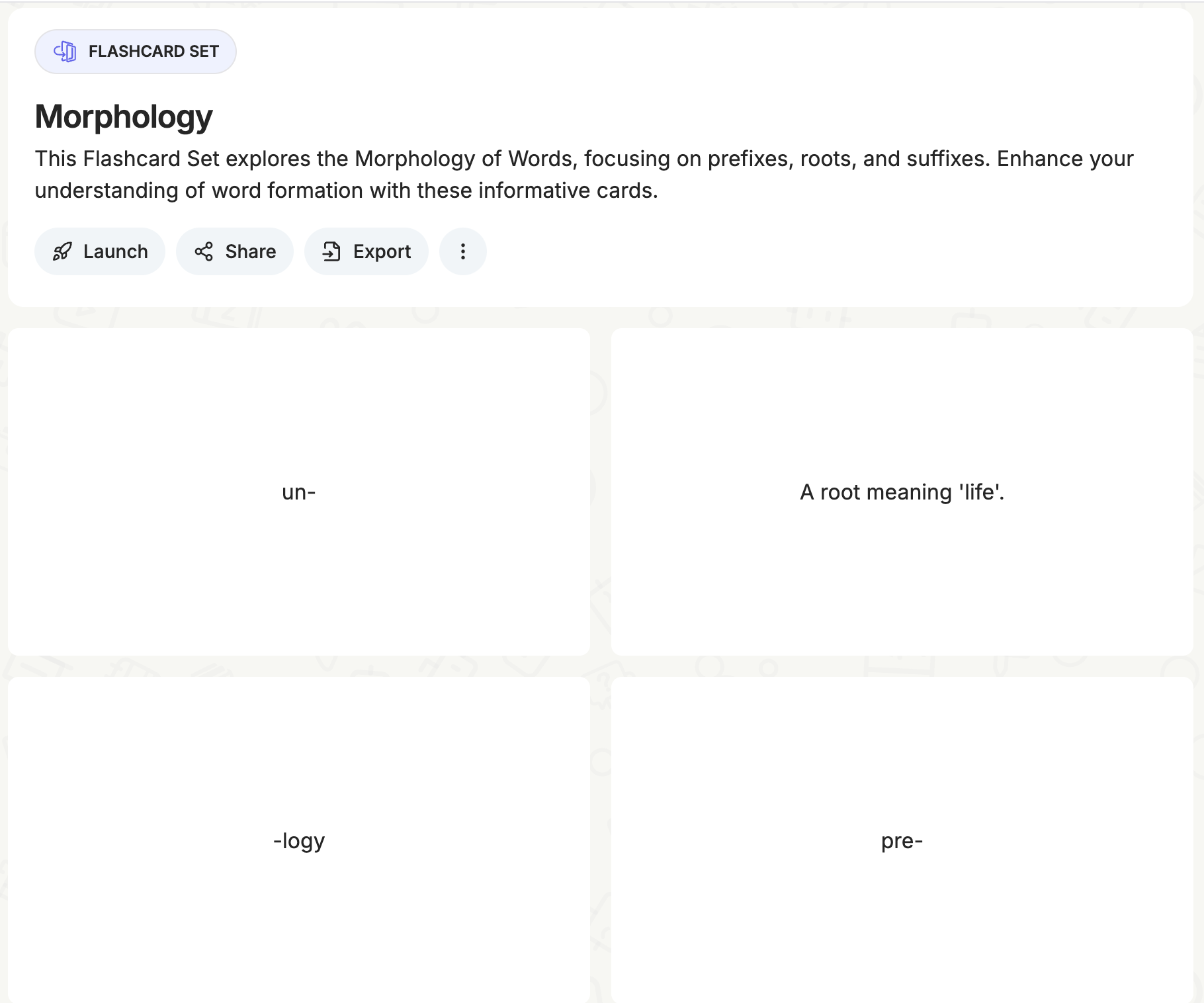
Another great Edcafe AI feature is its flashcards generator. Tying it in with morphology instruction, I have here an example where I prompted it to create a flashcard set solely on prefixes, suffixes, and roots.
Through this set, students can start on the basics, helping them be more familiarized in decoding words in morphology. Much like Edcafe AI-generated quizzes, flashcards can be launched and easily accessed via a QR code by students.
data-title="Get started with Edcafe AI for free"
data-description="Create AI lesson plans, slides, flashcards, images, chatbots, and more in seconds. Sign up for a forever free account today."
data-product="edcafe"
>
Food for Thought
As language continues to evolve, understanding the building blocks of words becomes increasingly essential. Morphology is more than just breaking down words. It is about recognizing the connections that shape meaning and influence how we communicate.
In the classroom, a deeper understanding of morphology opens up new opportunities for creativity and critical thinking. It can transform how we teach, how students learn, and how we engage with language in meaningful ways.
FAQs
What is morphology in language?
Morphology is the study of the structure of words. It focuses on how words are formed from smaller units of meaning called morphemes, including roots, prefixes, and suffixes.
How does understanding morphology help in teaching language?
Understanding morphology allows students to break down and analyze words at a deeper level. This enhances their vocabulary, spelling, and overall language comprehension, which improves reading and writing skills.
What are some examples of morphemes?
Morphemes can be classified as free morphemes (which can stand alone as words) and bound morphemes (which need to be attached to a free morpheme). For example, “un-” is a bound morpheme in “undo,” and “book” is a free morpheme.
Why is morphology important for students?
Morphology provides students with the tools to understand and deconstruct complex words, improving their ability to decode unfamiliar terms. This is particularly useful for expanding vocabulary and improving reading comprehension.
How does morphology relate to word formation and meaning?
Morphology directly impacts how words are formed and their meanings. By manipulating morphemes, we can change the meaning, tense, or part of speech of a word. For example, adding “-ness” turns an adjective (happy) into a noun (happiness).
Comments
Post a Comment